
At Home Owners Association, we understand the importance of being prepared for home repairs. Many homeowners wonder how much to save for home repairs and maintenance to avoid financial stress when unexpected issues arise.
In this blog post, we’ll explore various strategies to help you determine the right amount to set aside for home repairs. We’ll also discuss factors that can influence repair costs and provide practical tips for creating a robust savings plan.
How Much Should You Save Using the 1% Rule?
Understanding the 1% Rule
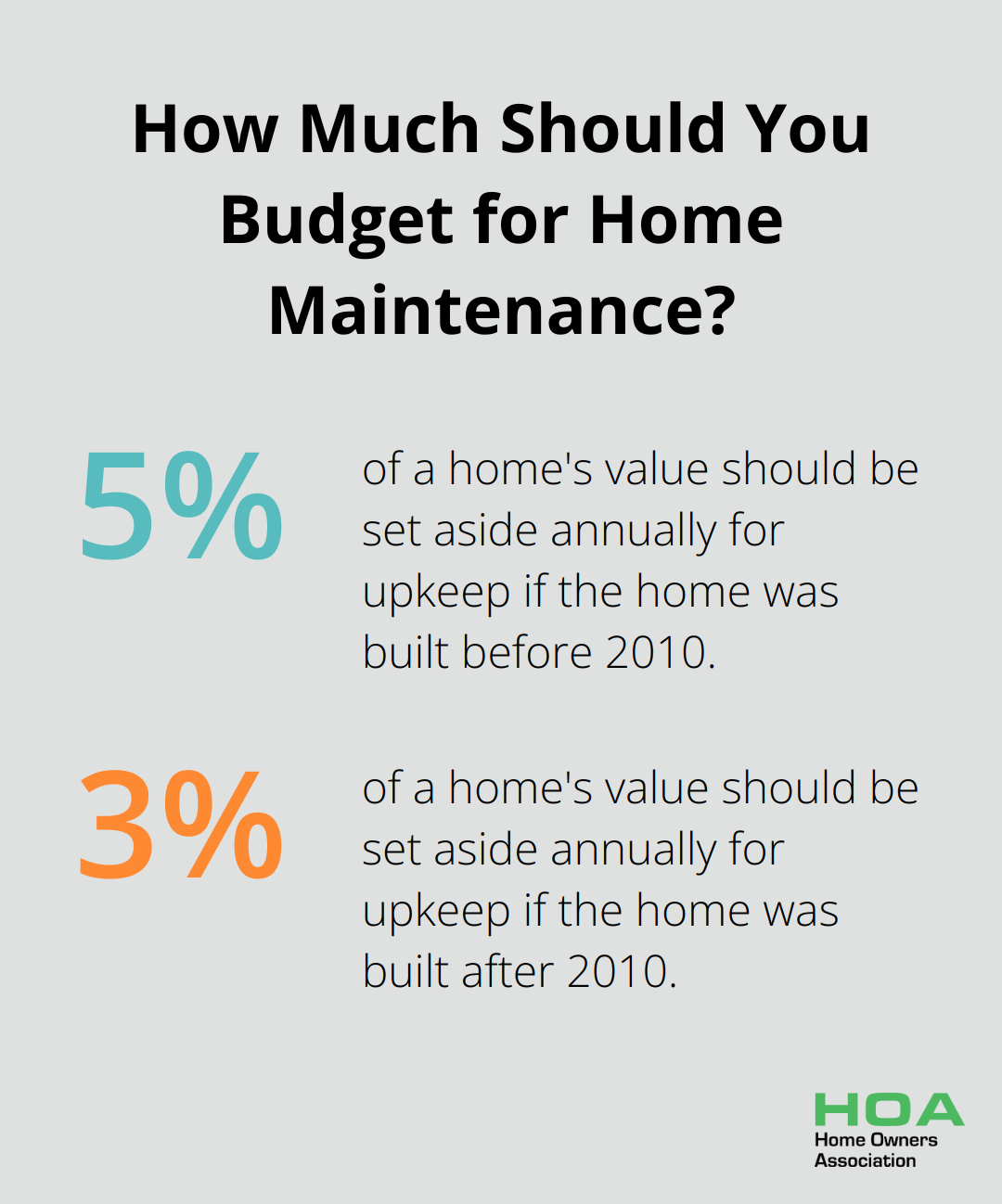
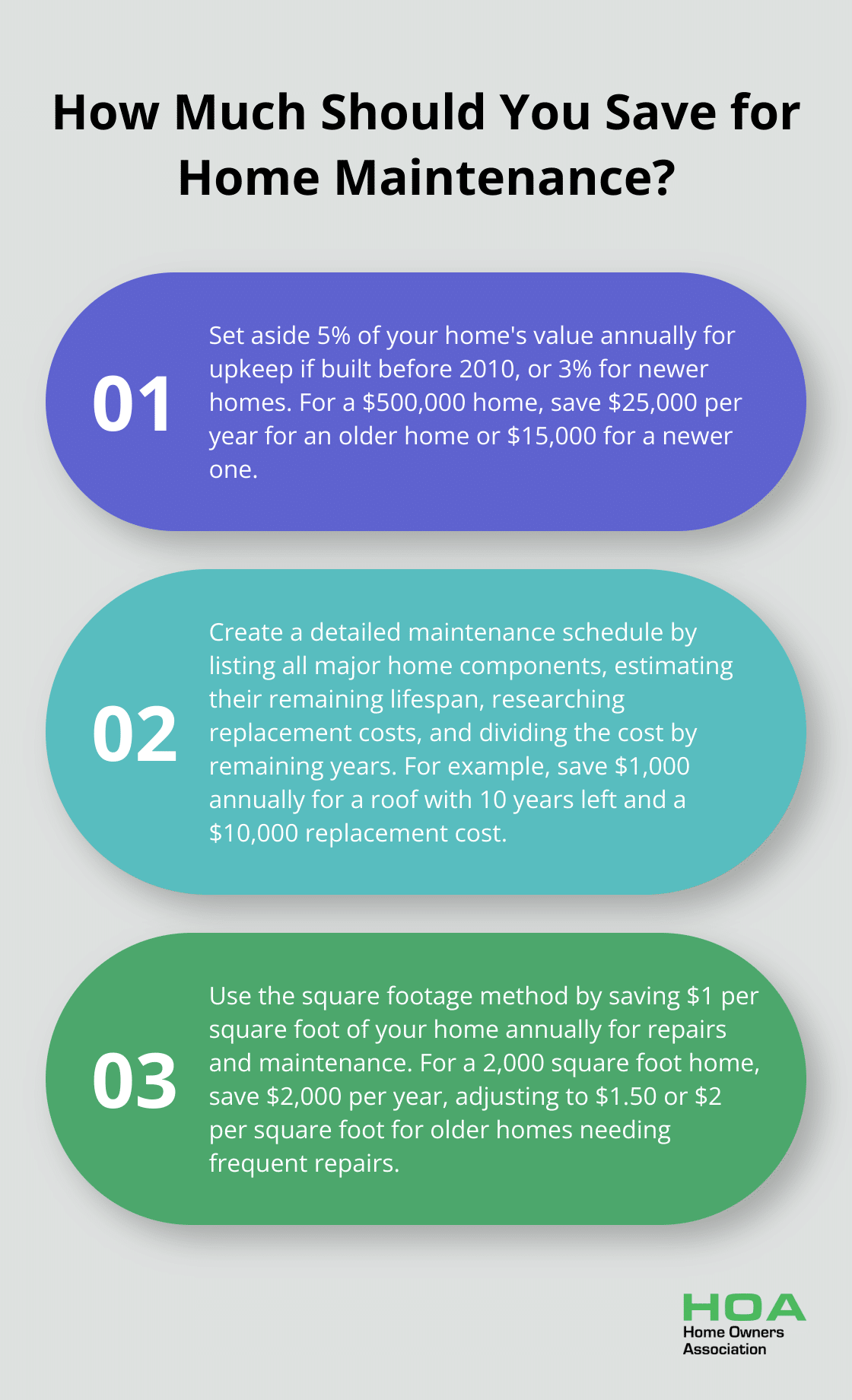
The 1% rule provides a straightforward guideline for estimating home repair and maintenance savings. This approach suggests you set aside 5% of your home’s value annually for upkeep if your home was built before 2010, or 3% for newer homes. For example, if your home is valued at $500,000, you should save $25,000 per year for an older home or $15,000 for a newer one. This method offers a clear way to budget for home maintenance.
Benefits of the 1% Rule
The primary advantage of this approach lies in its simplicity. It’s easy to calculate and provides a clear savings target. The rule also scales with your home’s value, which often correlates with the potential cost of repairs.
The National Association of Home Builders represents a large network of craftsmen, innovators, and problem solvers who build homes, enrich communities, and change lives. Their expertise can provide valuable insights into home maintenance and repair costs.
Considerations and Limitations
While this rule serves as a useful starting point, it’s not a universal solution. Older homes or those in harsh climates may require more savings annually. For instance, homes built before 2010 can average significantly higher annual repair expenses.
It’s also important to note that this rule doesn’t account for major renovations or upgrades. If you plan substantial improvements, you may need to save additional funds beyond this baseline.
Tailoring the Rule to Your Needs
We encourage you to use this rule as a minimum guideline. Consider factors like your home’s age, location, and condition when determining your savings goal. For instance, if you live in an area prone to extreme weather, you might try to save even more of your home’s value.
Regular maintenance can significantly reduce long-term repair costs. Use expert advice and resources to stay on top of your home’s needs and potentially lower your long-term expenses.
Moving Beyond the 1% Rule
While this rule provides a solid foundation, it’s essential to consider other factors that might influence your home repair savings strategy. In the next section, we’ll explore additional elements that can affect home maintenance costs and how to adjust your savings plan accordingly.
What Impacts Home Repair Costs?
Age and Condition of Your Home
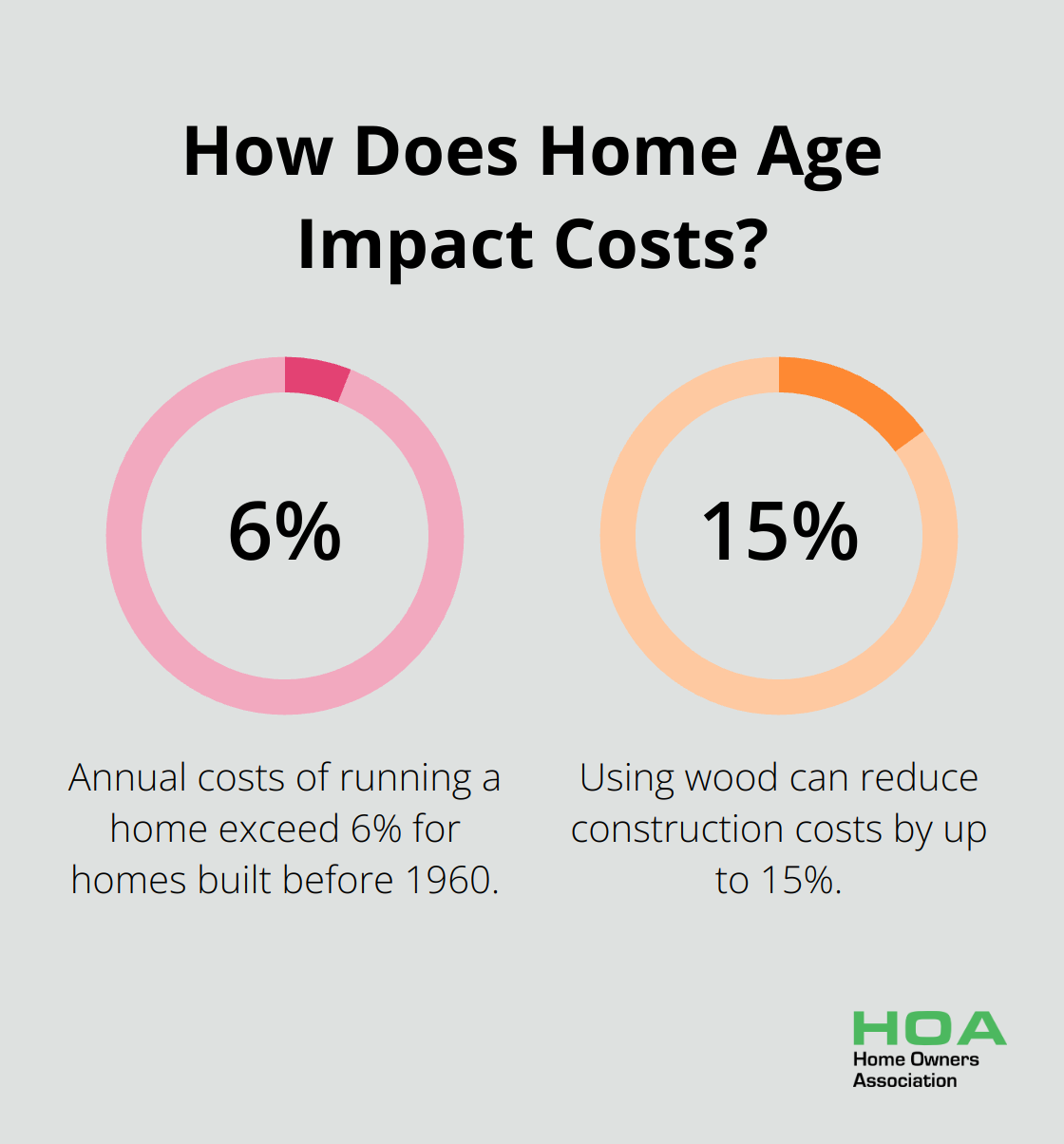
The age and condition of your home significantly influence repair costs. Older homes often require more frequent and expensive repairs. On average, annual costs of running a home amount close to 5% of the home’s value. This fraction exceeds 6% for homes built before 1960, compared to lower percentages for newer homes. This substantial difference underscores the need to consider your home’s age when planning your repair budget.
Climate and Weather Considerations
Your local climate plays a pivotal role in determining repair frequency and costs. Homes in areas with extreme weather conditions face more wear and tear. Coastal properties might need more frequent exterior maintenance due to salt air corrosion, while homes in regions with heavy snowfall could require additional roof maintenance.
The Insurance Information Institute reports that weather-related claims constitute a significant portion of home insurance payouts (indicating the impact of climate on home repair needs). While insurance may cover some weather-related damages, it’s prudent to budget for climate-specific maintenance to prevent larger issues.
Quality of Materials and Workmanship
The initial quality of your home’s construction and materials greatly affects long-term repair costs. Higher-quality materials and expert workmanship often result in fewer repairs over time. A well-installed roof using premium materials might last 20-30 years, while a lower-quality installation might need replacement in just 10-15 years.
When you plan renovations or repairs, investing in quality can lead to long-term savings. The National Association of Home Builders reports that using wood can reduce construction costs by up to 15%. Long-term savings are also possible with quality materials.
Importance of Regular Maintenance
Consistent upkeep is key to managing repair costs. Regular maintenance prevents small issues from becoming major problems. For instance, annual HVAC system checks (costing around $100-$200) can prevent system failures that might cost thousands to repair or replace.
Homeowners who follow a regular maintenance schedule often spend less on emergency repairs. Create a yearly maintenance checklist and stick to it to significantly reduce your overall repair costs over time.
Impact of Home Size and Complexity
The size and complexity of your home also affect repair costs. Larger homes naturally have more components that could require maintenance or repair. Homes with complex architectural features, such as multiple roof lines or custom windows, may incur higher repair costs due to specialized labor and materials.
Consider these factors when budgeting for home repairs. In the next section, we’ll explore alternative savings strategies that take these variables into account, helping you create a more tailored approach to your home repair savings plan.
Beyond the 1% Rule: Tailored Savings Strategies
The Square Footage Method
An effective alternative to the 1% rule is the square footage method. This approach recommends setting aside $1 per square foot of your home annually for repairs and maintenance. For a 2,000 square foot home, you should save $2,000 per year. This method works well for homes with unique features or layouts that might not align with the home’s overall value.
You can adjust this method based on your home’s condition. For older properties or those needing frequent repairs, increase the amount to $1.50 or $2 per square foot. Newer homes or those in excellent condition might require less (perhaps $0.75 per square foot).
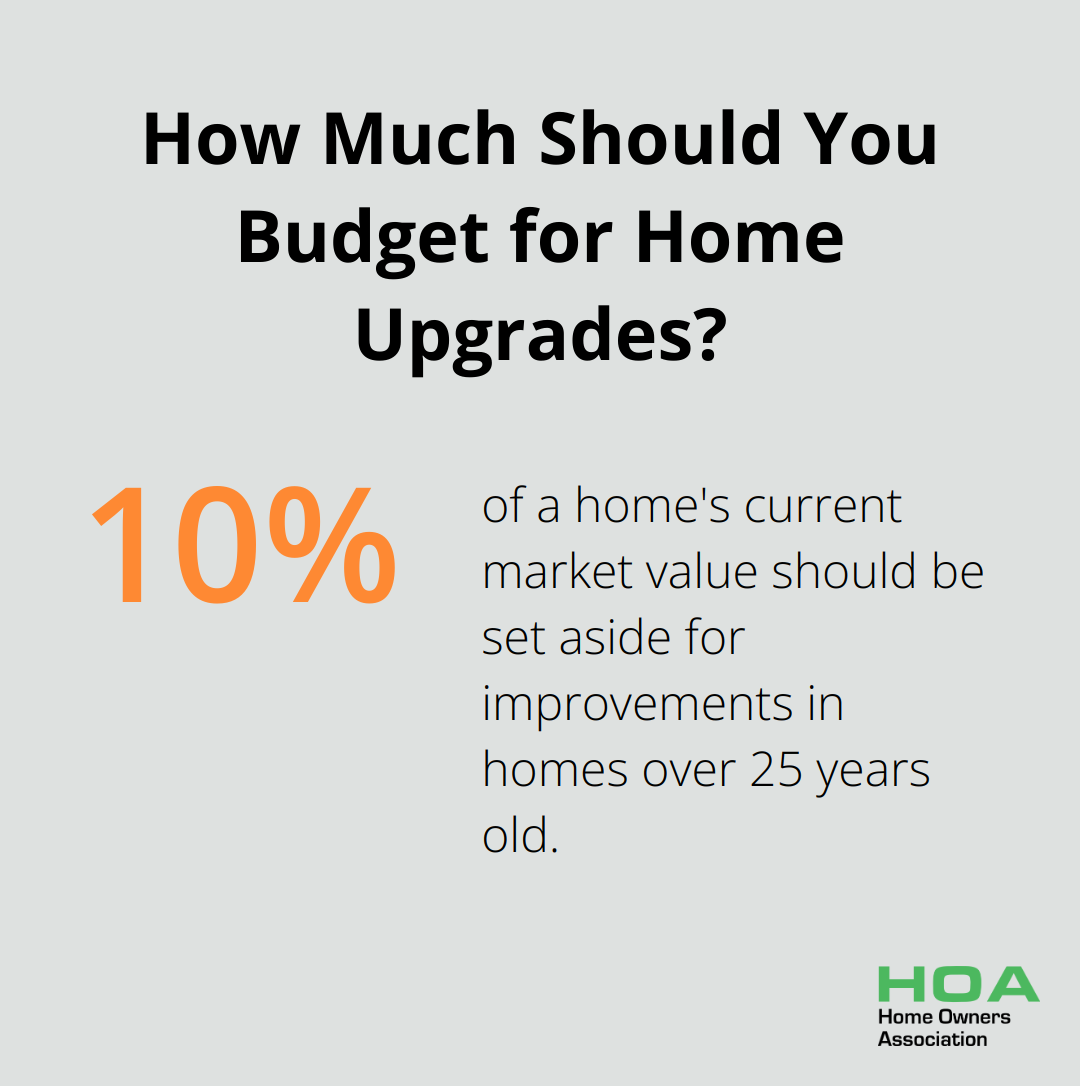
The 10% Rule for Older Homes
Homes over 25 years old often benefit from the 10% rule. This strategy involves setting aside 10% of your home’s current market value for improvements overall. This method acknowledges that older homes often require more frequent and costly repairs. It also scales with your overall housing budget, which can more accurately reflect your home’s maintenance needs than its market value alone.
Creating a Detailed Maintenance Schedule and Budget
A customized maintenance schedule and budget based on your home’s specific components offers the most precise approach. This strategy involves:
- List all major systems and components in your home (roof, HVAC, appliances, etc.)
- Estimate the remaining lifespan of each item
- Research the replacement cost for each
- Divide the replacement cost by the remaining years of life
For example, if your roof has 10 years left and will cost $10,000 to replace, you should save $1,000 per year for this specific item. Repeat this process for all major components, then add up the annual savings needed for each to get your total yearly savings goal.
This method requires more initial effort but provides the most accurate and personalized savings plan. It also helps you anticipate and prepare for major expenses well in advance.
Adapting Your Strategy
The key to effective home repair savings is to find a strategy that aligns with your specific circumstances and to stick to it consistently. Regular maintenance and proactive savings can prevent financial stress when repairs are needed and keep your home in top condition for years to come.
Consider factors such as your home’s age, location, and unique features when choosing a savings strategy. You might even combine elements from different methods to create a tailored approach that works best for your situation. For example, if you own a home in Melbourne, you might need to adjust your budget based on local market conditions and maintenance costs.
Final Thoughts
Planning for home repairs and maintenance is an essential part of homeownership. We explored various strategies to determine how much to save for home repairs and maintenance, including the 1% rule, square footage method, and 10% rule for older homes. The best choice depends on your specific circumstances and home characteristics.
Regular maintenance plays a vital role in managing repair costs effectively. Addressing small issues promptly prevents them from escalating into major, expensive problems. This proactive approach saves money in the long run and helps maintain your home’s value and comfort.
At Home Owners Association, we support homeowners in Melbourne, Australia with their home maintenance and improvement needs. Our members receive trade pricing, discounts on materials, and expert advice (ensuring their projects meet the highest standards). You can confidently manage your home’s upkeep and enjoy the benefits of a well-maintained property for years to come.





