
At Home Owners Association, we understand the growing importance of sustainable construction in today’s world. Choosing the most eco-friendly building materials is a critical step towards reducing environmental impact and creating healthier living spaces.
In this post, we’ll explore various sustainable options and provide guidance on selecting the best eco-friendly building materials for your projects. Our aim is to help you make informed decisions that benefit both your home and the planet.
What Are Eco-Friendly Building Materials?
Definition and Importance
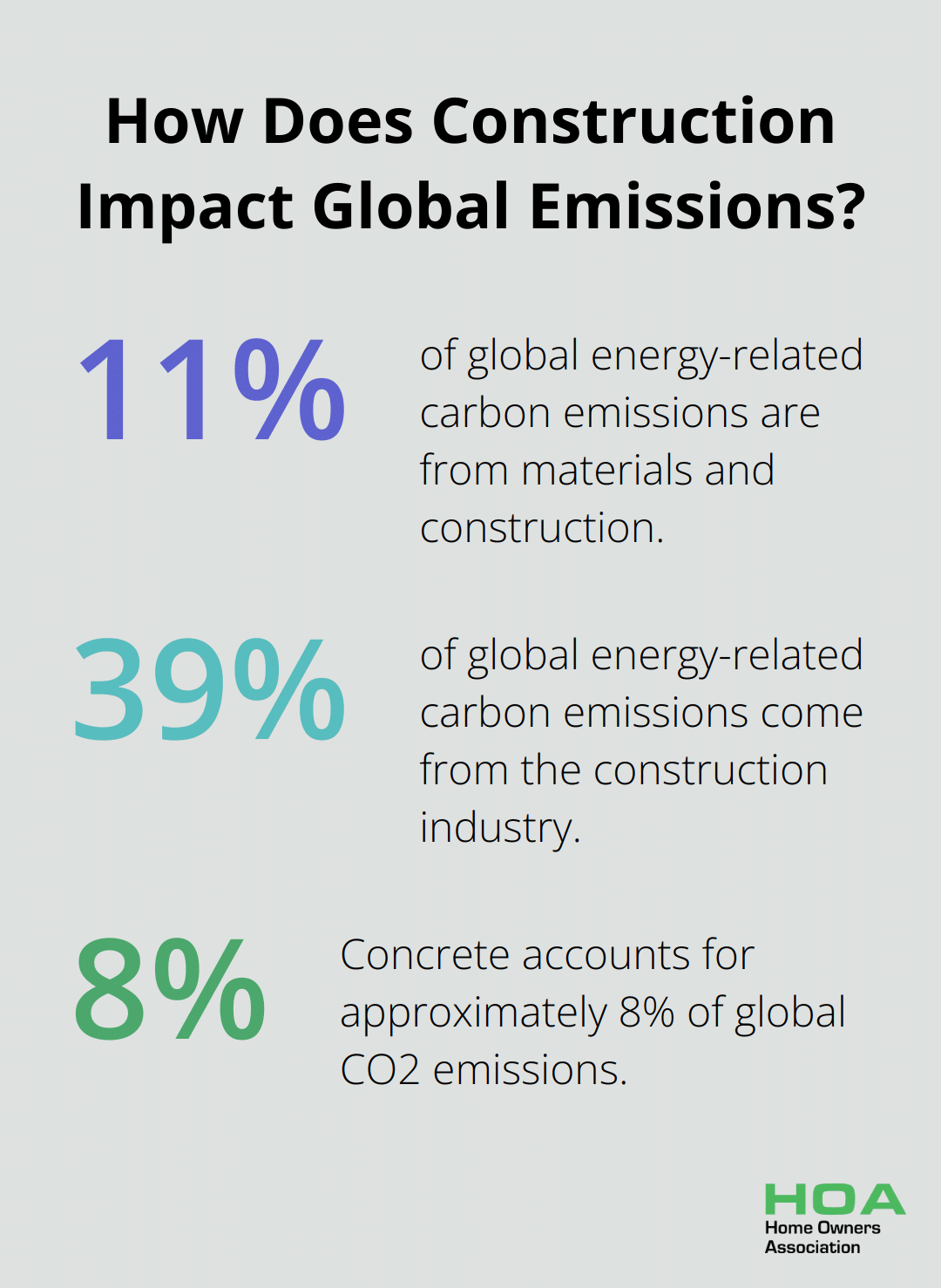
Eco-friendly building materials form the foundation of sustainable construction. These materials minimize environmental impact throughout their lifecycle, from production to disposal. The construction industry’s significant contribution to global CO2 emissions (39% of global energy-related carbon emissions: 28% from operational emissions, from energy needed to heat, cool and power buildings, and 11% from materials and construction) underscores the importance of adopting sustainable practices.
The Environmental Cost of Traditional Materials
Traditional building materials often carry a substantial environmental burden. Concrete, for example, accounts for approximately 8% of global CO2 emissions. Steel production generated about 2.6 billion tons of CO2 emissions in 2020. These statistics highlight the urgent need for alternatives to reduce our carbon footprint.
Benefits of Sustainable Construction
Sustainable construction offers numerous advantages:
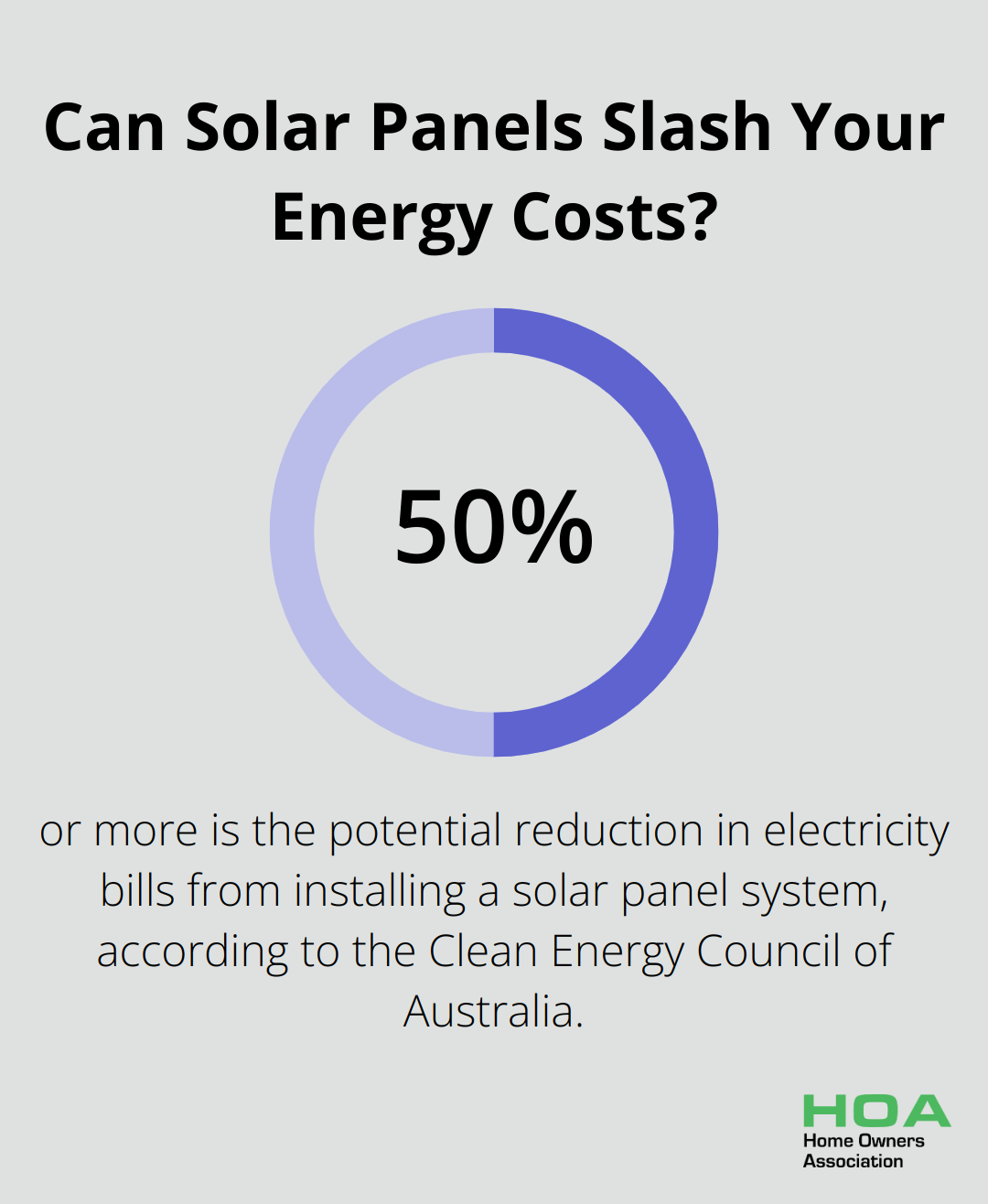
- Energy Efficiency: Designs incorporating eco-friendly materials can reduce heating and cooling bills by up to 50%.
- Cost Savings: While initial costs may be higher, long-term savings often offset this investment.
- Improved Indoor Air Quality: Sustainable materials typically emit fewer toxins, contributing to healthier living spaces.
- Reduced Environmental Impact: Lower carbon emissions and resource consumption benefit the planet.
Selecting the Right Materials
When choosing eco-friendly building materials, consider their entire lifecycle:
- Production Energy: Assess the energy required for manufacturing.
- Transportation Emissions: Consider the distance materials travel to reach the construction site.
- Recyclability: Evaluate the potential for recycling or biodegradation at the end of the material’s life.
For example, bamboo (a rapidly renewable resource) grows back in just 3-5 years and is 100% biodegradable.
Certifications and Local Sourcing
Look for established environmental certifications when selecting materials. Labels such as FSC® for responsibly sourced timber or GECA for products that have undergone comprehensive lifecycle assessments provide assurance of sustainability standards.
Opting for locally sourced materials can significantly reduce transportation-related emissions (and often supports local economies). This approach aligns with the growing trend of prioritizing regional options in construction projects.
As we move towards more sustainable building practices, the next section will explore some of the top eco-friendly building materials available in the market today.
Top Eco-Friendly Building Materials for Your Next Project
Recycled Steel: Strength Meets Sustainability
Recycled steel stands as a powerhouse in sustainable construction. It outperforms plastic, paper, aluminum, and glass combined as the most recycled material globally. Your project can significantly reduce carbon emissions by incorporating recycled steel. Every tonne of scrap used for steel production avoids the emission of 1.5 tonnes of carbon dioxide, and the consumption of 1.4 tonnes of iron ore and 740 kg of coal.
Bamboo: The Rapid Renewable
Bamboo has surged in popularity as a sustainable alternative to traditional timber. It matures in just 3-5 years, a fraction of the time hardwoods require. Its strength-to-weight ratio rivals steel, making it suitable for various applications. As a 100% biodegradable material, bamboo ensures minimal environmental impact at the end of its lifecycle.
Reclaimed Wood: Character and Conservation
Reclaimed wood offers both sustainability and unique aesthetics. You reduce demand for new timber and preserve a piece of history by repurposing wood from old buildings. The Forest Stewardship Council (FSC®) certification helps ensure sustainable sourcing. Reclaimed wood often boasts superior strength due to its age and adds distinctive character to projects.
Hempcrete: Innovative and Carbon-Negative
Hempcrete, a biocomposite made from hemp hurds and lime, presents an innovative solution for sustainable construction. Evidence supports that hempcrete can be considered a carbon-negative material. Hempcrete provides excellent insulation, regulates humidity, and resists mold and pests.
Earth Blocks: Ancient Wisdom, Modern Application
Earth blocks (also known as compressed earth blocks or CEBs) combine soil, clay, and other natural materials. This age-old building technique has seen a resurgence due to its low environmental impact and energy efficiency. Earth blocks offer excellent thermal mass, helping to regulate indoor temperatures naturally.

The selection of eco-friendly materials requires consideration of their entire lifecycle (from production to disposal). We recommend looking beyond initial costs and evaluating long-term benefits such as energy efficiency, durability, and potential for future recycling. These sustainable options not only benefit the environment but also often result in healthier living spaces and long-term cost savings.
As we explore the factors that influence the selection of eco-friendly building materials, you’ll gain a deeper understanding of how to make informed decisions for your sustainable construction projects.
How to Evaluate Eco-Friendly Building Materials
Lifecycle Assessment
A comprehensive lifecycle assessment (LCA) is essential when evaluating eco-friendly materials. This process calculates the environmental impact of products or services throughout their entire lifecycle. Bamboo might appear ideal due to its rapid growth, but if sourced from distant locations, the transportation emissions could negate its benefits. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) provides guidelines for conducting LCAs, which can help you make more informed decisions.
Energy Efficiency
The energy efficiency of a material extends beyond its insulation properties. Consider the embodied energy – the total energy required to produce, transport, and install the material. Recycled steel has a lower embodied energy compared to virgin steel. The carbon footprint of steel is 1.4 tons per produced ton of steel according to IEA, and 1.85 according to McKinsey and the World Steel Association. When selecting insulation materials, look for options with high R-values per inch (such as sheep’s wool or cellulose), which can significantly reduce heating and cooling costs over time.
Durability and Maintenance
Long-lasting materials that require minimal maintenance often prove the most sustainable choices. Fiber cement siding can last up to 50 years with proper care, compared to vinyl siding which typically needs replacement after 20-30 years. When considering wood products, opt for those treated with non-toxic preservatives to extend their lifespan without harmful environmental impacts. Durability often translates to cost-effectiveness in the long run, despite potentially higher upfront costs.
Local Availability and Transportation
Sourcing materials locally reduces transportation emissions and supports regional economies. The Australian government’s Green Building Council emphasizes the importance of using materials within a 400km radius of the construction site to minimize environmental impact. When local options are limited, consider materials with a high value-to-weight ratio to optimize transportation efficiency. Lightweight insulation materials like aerogel can provide excellent thermal performance while minimizing shipping costs and emissions.
Cost-Effectiveness and Long-Term Value
While initial costs matter, it’s important to consider the long-term value of eco-friendly materials. Energy-efficient options may have higher upfront costs but can lead to significant savings over time. Installing a solar panel system can reduce electricity bills by up to 50% or more (according to the Clean Energy Council of Australia). Additionally, many eco-friendly materials, such as bamboo flooring or recycled glass countertops, can increase property value due to growing consumer demand for sustainable homes.
Final Thoughts
Sustainable construction has become a necessity for our planet’s future. The most eco-friendly building materials offer diverse and innovative options, from recycled steel to bamboo, each with unique benefits. Homeowners who select these materials can enjoy improved indoor air quality, reduced energy costs, and increased property values.

Evaluating eco-friendly materials requires a holistic approach, considering their entire lifecycle and long-term value. Energy efficiency, durability, and recyclability play vital roles in determining a material’s true sustainability. Local sourcing reduces transportation emissions and supports regional economies, creating a positive impact in our communities.
Home Owners Association supports Melbourne homeowners in their sustainable building projects. Our members receive trade pricing and discounts on construction materials (including eco-friendly options), expert advice, and educational resources. We encourage you to embrace sustainable building practices and create homes that are beautiful, functional, and kind to our planet.





