
At Home Owners Association, we’re committed to promoting sustainable living practices. As the construction industry evolves, understanding what sustainable building practices are has become essential for homeowners and builders alike.
These practices not only reduce environmental impact but also offer long-term economic benefits and improve occupant health. In this post, we’ll explore the key elements of sustainable building and how they can be implemented in your next construction project.
What Are Sustainable Building Practices?
Definition and Core Principles
Sustainable building practices are construction methods that minimize environmental impact while maximizing resource efficiency and occupant well-being. These practices have gained significant traction in recent years, driven by growing environmental awareness and the long-term cost benefits they offer.

The core of sustainable construction revolves around three key principles:
- Environmental stewardship
- Economic prosperity
- Social responsibility
This approach uses resources wisely, reduces waste, and creates buildings that are not only eco-friendly but also economically viable and beneficial to the community.
Environmental Benefits
The environmental advantages of sustainable building are substantial. Buildings are currently responsible for 39% of global energy related carbon emissions: 28% from operational emissions, from energy needed to heat, cool and power them, and 11% from materials and construction. Adopting sustainable practices can significantly reduce this figure. For instance, energy-efficient designs can cut a building’s energy consumption by 30-50% (as reported by the Environmental Protection Agency).
The use of recycled materials also plays a crucial role in reducing landfill waste. The Construction & Demolition Recycling Association states that recycling concrete alone saves 140 million tons from landfills annually in the U.S.
Water conservation is another important aspect of sustainable building. Low-flow fixtures and rainwater harvesting systems can reduce water usage by up to 15% (according to the U.S. Green Building Council). This not only preserves a vital resource but also lowers utility bills for homeowners.
Economic Advantages
While the initial costs of sustainable building might be higher, the long-term savings are significant. The World Green Building Council reports that there has been a steady growth since 2012 in the number of owners who see a 10% or greater increase in asset value for new green buildings. Moreover, they have lower operating costs, with energy savings of 20-30% common in the first year alone.
Social Impact
Sustainable buildings also have a positive social impact. They create healthier living environments with better air quality, natural lighting, and non-toxic materials. A study by the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health found that occupants of green-certified buildings have 26% higher cognitive function scores and 30% fewer sick building symptoms.
The implementation of these practices doesn’t just result in the construction of homes; it creates healthier, more efficient, and more valuable living spaces for communities. Organizations like Home Owners Association (which has been serving Australia since 1980) are committed to guiding their members towards these sustainable solutions, ensuring they reap the benefits of this forward-thinking approach to construction.
As we move forward, it’s important to understand the essential elements that make up sustainable building design. Let’s explore the key components that contribute to creating truly sustainable structures.
Essential Elements of Sustainable Building
Energy Efficiency and Renewable Integration
Energy efficiency forms the foundation of sustainable building. Buildings consume about 40% of the total energy used in the United States (U.S. Department of Energy). We can reduce this consumption significantly through energy-efficient designs.
Proper insulation is a key starting point. Homeowners can save an average of 15% on heating and cooling costs by air sealing their homes and adding insulation (Environmental Protection Agency). This translates to approximately $200 in annual savings for the average American household.
Renewable energy sources, particularly solar panels, have become more accessible and efficient. The cost to install solar has dropped by more than 70% over the last decade (Solar Energy Industries Association). Many homeowners report substantial savings on their energy bills after installing solar panels.
Water Conservation Strategies
Water conservation plays a vital role in sustainable building. The average American family uses more than 300 gallons of water per day at home (Environmental Protection Agency). Water-saving fixtures can reduce this figure dramatically.
Low-flow toilets use 1.28 gallons per flush or less, compared to older models that use up to 6 gallons. This change can save a family of four up to 13,000 gallons of water annually. Water-efficient showerheads can save the average family nearly 3,000 gallons of water per year.
Rainwater harvesting systems offer another effective strategy. These systems can collect up to 600 gallons of water from 1 inch of rain on a 1,000 square foot roof. This collected water can serve irrigation purposes, reducing the demand on municipal water supplies.
Eco-Friendly Materials
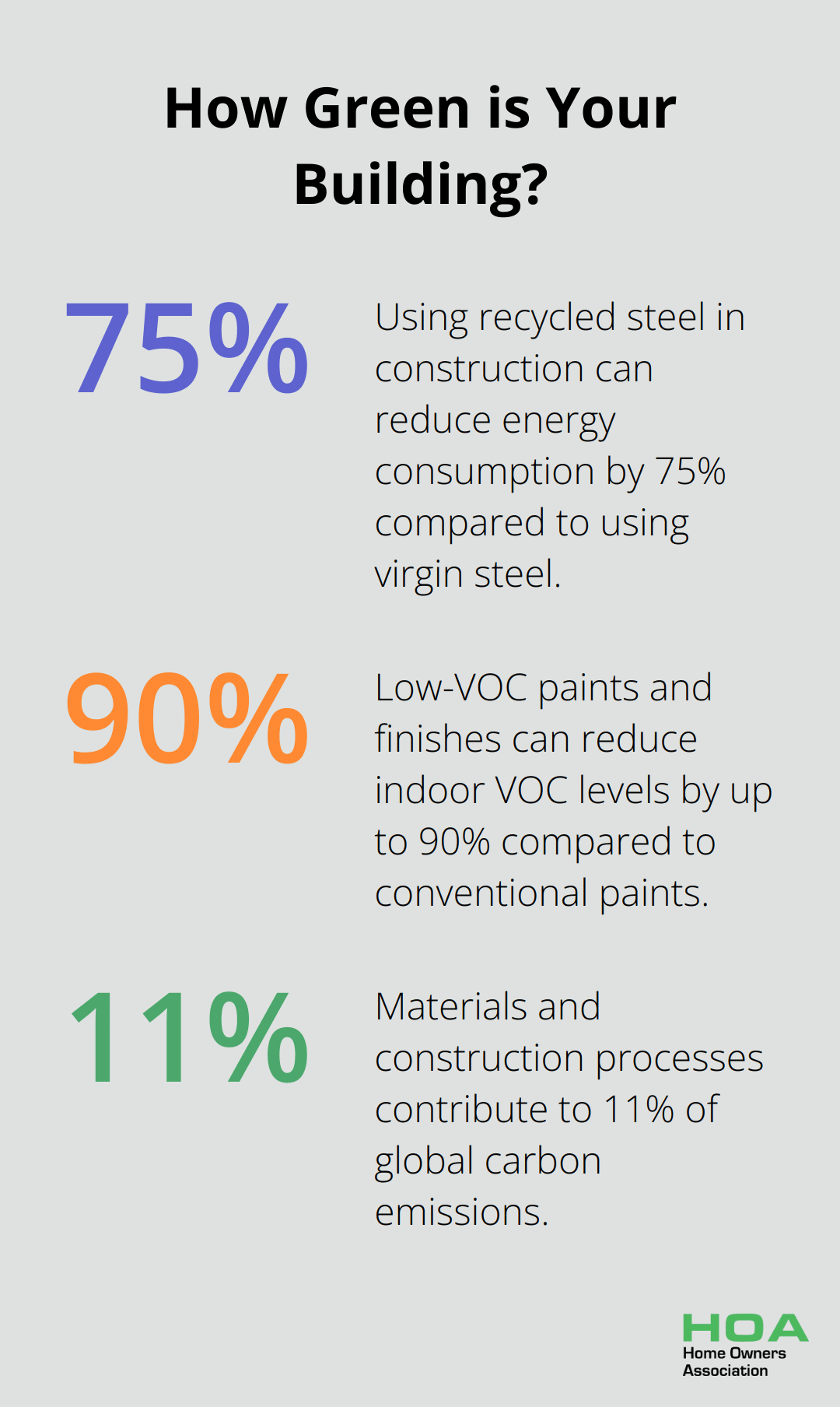
The choice of building materials significantly impacts a structure’s sustainability. Materials and construction processes contribute to 11% of global carbon emissions (World Green Building Council).
Recycled steel stands out as an excellent eco-friendly option. As the most recycled material on the planet (Steel Recycling Institute), using recycled steel in construction can reduce energy consumption by 75% compared to using virgin steel.
Bamboo has gained popularity as a sustainable material. It grows up to 35 inches per day, making it one of the fastest-growing plants on Earth. Bamboo flooring offers durability and attractiveness, and can be harvested every 3-5 years (unlike hardwoods which can take 20-120 years to mature).
Indoor Air Quality and Occupant Health
Indoor air can be two to five times more polluted than outdoor air (Environmental Protection Agency). This fact makes indoor air quality a critical consideration in sustainable building.
Low-VOC (Volatile Organic Compounds) paints and finishes emit fewer harmful chemicals, improving indoor air quality. These products can reduce indoor VOC levels by up to 90% compared to conventional paints (Green Seal organization).
Proper ventilation is equally important. The American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE) recommends a minimum of 0.35 air changes per hour for residential buildings. This can be achieved through mechanical ventilation systems or strategically placed windows for natural ventilation.
The implementation of these sustainable building practices not only benefits the environment but also creates healthier, more comfortable living spaces. As we move forward, it’s important to understand how to put these elements into practice effectively. Let’s explore the practical steps for implementing sustainable building practices in the next section.
How to Implement Sustainable Building Practices
Choosing the Right Certification
Green building certification systems provide a framework for implementing sustainable practices. The two most recognized systems are LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) and BREEAM (Building Research Establishment Environmental Assessment Method). LEED, developed by the U.S. Green Building Council, is used in North America and has certified over 80,000 projects across 162 countries. BREEAM, originating in the UK, has certified over 594,000 buildings across 89 countries.
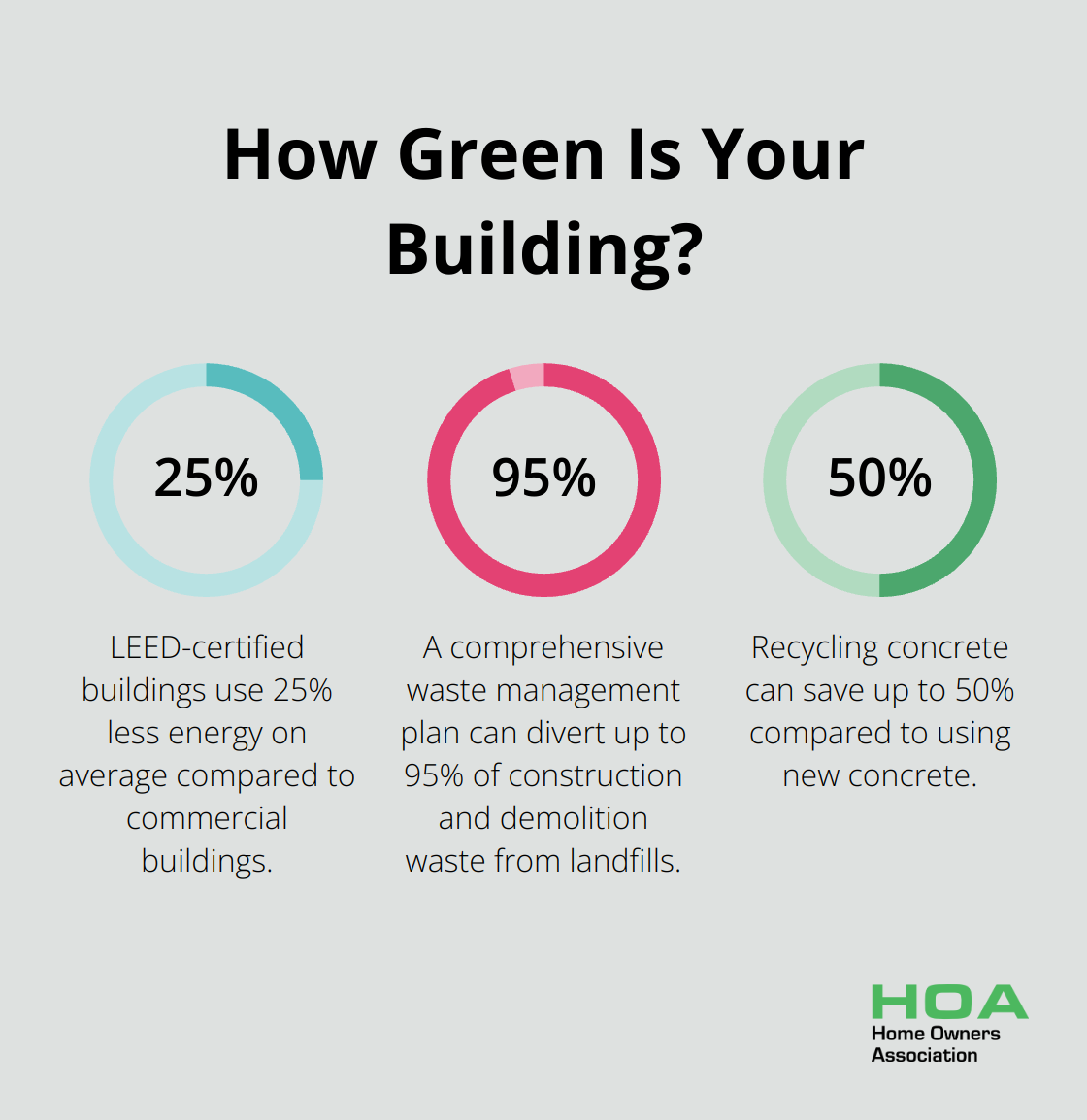
These certifications offer a roadmap for sustainable construction, covering aspects like energy efficiency, water usage, and material selection. While certification can add to initial costs, certified buildings often see higher property values and lower operating costs. LEED-certified buildings use 25% less energy on average compared to commercial buildings and have an average ENERGY STAR score of 89/100.
Smart Site Selection and Development
Sustainable building starts with choosing the right location. Ideal sites minimize environmental impact and maximize energy efficiency. For example, orienting a building to take advantage of natural sunlight can reduce lighting and heating costs by up to 30%.
When developing a site, it’s important to preserve existing trees and vegetation. A mature tree can absorb up to 48 pounds of carbon dioxide annually, which helps offset the carbon footprint of construction. Additionally, the use of permeable paving materials for driveways and walkways can reduce stormwater runoff by up to 90%, which prevents erosion and protects local water systems.
Effective Waste Management
Construction and demolition activities generated over 600 million tons of waste in the United States in 2018, according to the EPA. A comprehensive waste management plan can divert up to 95% of this waste from landfills.
Strategies include on-site sorting of recyclable materials, use of prefabricated components to reduce on-site waste, and partnerships with local recycling facilities. Recycling concrete can save up to 50% compared to using new concrete, while also reducing landfill waste.
Ensuring Long-Term Efficiency
The sustainability of a building extends far beyond its construction. Proper maintenance and operational practices are essential for long-term efficiency. Smart home systems can lead to energy savings of 10-30% (according to the U.S. Department of Energy). Regular maintenance of HVAC systems can improve their efficiency by 15-20%.
It’s important to educate homeowners on proper maintenance and efficient use of their sustainable features. Comprehensive guides and resources can help homeowners maximize the benefits of their sustainable homes.
Collaboration with Experts
Implementing sustainable building practices often requires specialized knowledge. Collaboration with sustainability consultants, energy auditors, and green building experts can ensure that projects meet the highest standards of sustainability. These professionals can provide valuable insights on the latest technologies and best practices in sustainable construction.
Final Thoughts
Sustainable building practices are not just a trend; they represent a necessity for our planet’s future. These practices encompass energy efficiency, water conservation, eco-friendly materials, and healthy indoor environments. The implementation of what are sustainable building practices creates buildings that benefit the environment, economy, and society.

The future of sustainable construction looks promising with advancements in materials science and smart home technologies. We expect to see stricter regulations and higher standards for sustainable building as climate change concerns grow. Modular and prefab construction methods continue to reduce waste and improve efficiency in the industry.
We at Home Owners Association support our members in their journey towards sustainability. Our resources and expert advice can help you navigate the world of sustainable building with confidence. Every step towards sustainability counts, whether you plan a new build, a renovation, or simply want to improve your home’s efficiency.





